Which of the Following Administration Routes Is Not Parenteral
Enteral via the gastrointestinal tract. Other less frequent routes specialized parenteral routes are summarized below.

Comparison Of Three Different Routes Of Drug Administration Oral Download Scientific Diagram
Wiki User 2012-06-17 031220.
. Start studying Chapter 11. Difficult to remove is dose is toxic. Intravenous intramuscular or subcutaneous.
Factors affecting selection of route. Administration by injection parenteral administration includes the following routes. Parenteral via any route that does not involve the GI tract.
Terms in this set 40 Parental routes-includes any other route other than the gastrointestinal tract. The most important and most frequently used parenteral routes are intravenous route IV intramuscular route IM and subcutaneous route SC. Intravenous intramuscular topical otic conjunctival nasal inhalation and subcutaneous are parenteral routes of administration.
Topical administration is a parenteral route that does not require sterile formulations. Four Routes of Parenteral Administration and Approved Abbreviation. YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE.
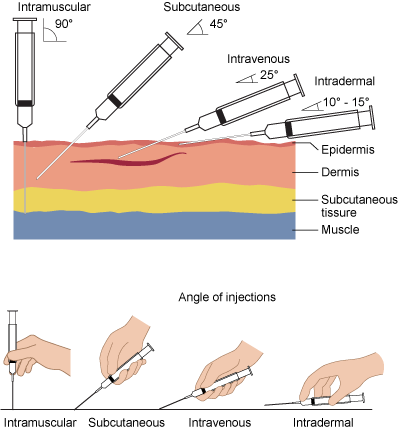
Subcutaneous SQ 45 Degrees Angle. A vomiting sick person will best treated by this method A Intravenous B Buccal C None D Oral. Intradermal ID 15 Degrees Angle.
Sublingual The key C is correct because parenteral routes of administration bypass the gastrointestinal tract and subcutaneous administration involves injection into the fatty layer under the skin. Drug- and patient-related factors determine the selection of routes for drug administration. Characteristics of the drug.
Parenteral routes of drug administration are a means of introducing a drug into the body through injection for quicker absorption by the body. Intravenous IV 10 - 15 Degree Angle. All of the following are parenteral routes of drug administration EXCEPT.
A intravenous intramuscular and subcutaneous. Subcutaneous under the skin Intramuscular in a muscle Intravenous in a vein Intrathecal around the spinal cord. D intravenous intramuscular and intraperitoneal.
The IV administration provides immediate access of the drug to the sys-temic circulation resulting in the rapid onset of drug action. Topical via the skin. B intravenous intramuscular and sublingual.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Preferred for rapid absorption useful for when patient is unconscious un-cooperative or unable to take drug by an enteral route. Intravenous injection is the most common parental route of medication administration and has the benefit of bypassing the first-pass metabolism by the liver.
Beside above is inhalation a parenteral route. Distractor A means that medication is dissolved between the cheek and gum distractor B typically implies that a medication is swallowed. One of these cannot be used to administer drug in an unconscious patient A Parenteral B Oral C None D Rectal.
Intramuscular IM 90 Degrees Angle. Risks involved with invading the body with a needle. Administration by the Parenteral Route.
The two most frequent routes for. The common routes of parenteral administration are intramuscular IM subcutaneous and IV. What are the 4 parenteral routes for drug administration.
Enteral route involves absorption of the drug via the gastrointestinal tract and includes oral sublingual and rectal administration. SC route is often. To answer this question we must review the following 5.
A 09 NaCl b 045 NaCl c D509 NaCl d D502 NaCl. Generally we can classify routes of administration into three broad categories. You may ask why is one route of administration chosen over another.
C intradermal intrathecal and intraperitoneal. Selection of a parenteral route of administration for a new therapeutic moiety depends on several considerations such as Desired rate of onset of action. Disadvantages of parenteral routes.
Given their superficial location on the skin peripheral veins provide easy access to the circulatory system and are often utilized in the parenteral administration of medications. A Parenteral administration B Dermal administration C Enteral administration D Sublingual administration. Site of action of the druglocal or systemic.
Condition of the patient unconscious vomiting diarrhoea. In addition parenteral routes of administration include dosage forms such as sublingual tablets transdermal patches and inhalerswhich will not be discussed in this chapter. Parenteral route on the other hand refers to any routes of administration that do not involve drug absorption via the gastrointestinal tract par around enteral gastrointestinal including injection routes eg intravenous route.
This involves the administration of a drug within the vertebral column. The intravenous route of medication is given directly into a vein. Since oral buccal sublingual and rectal comprise the enteral routes of administration any other route is considered a parenteral administration site.
IV route provides the most rapid onset of action whereas the SC IM and IP routes have slower rate of drug absorption into the systemic circulation. Most of the drugs can be administered by different routes. Of the following IV solutions which one is the most hypertonic.
The parenteral routes of administration are used for various reasons.

Parenteral Vs Non Parenteral Administration Routes Parenteral Administration Literally Means Administered In The Space Between The Enteric Canal The Ppt Download

7 2 Parenteral Medications And Preparing Medications From Ampules And Vials Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care

Route Of Administration Wikiwand

What Are The Different Routes For Drug Administration Gafacom
No comments for "Which of the Following Administration Routes Is Not Parenteral"
Post a Comment